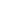
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water.[1] An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided.[2] Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific (the largest), Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic (the smallest).[3][4] Seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km2 (139,000,000 sq mi) of the planet. The ocean is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, and therefore integral to life on Earth. Acting as a huge heat reservoir, the ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle. ทางเข้าบาคาร่าได้เงินจริง
The ocean is a vast body of saltwater that covers about 71% of the Earth's surface. It plays a crucial role in supporting life on our planet and is an integral part of the Earth's hydrosphere, which includes all water found on or under the surface.
Key characteristics of the ocean include:
-
Saltwater Composition: The water in the ocean contains various dissolved salts, primarily sodium chloride (common table salt). This saltiness is the reason why the ocean is called "saltwater."
-
Global Connectivity: The ocean is not confined to specific regions; it connects all continents and is interconnected through various currents and water movements. This global interconnectivity influences weather patterns and climate across the Earth.
-
Depth Variability: The ocean is incredibly deep, with some areas reaching depths of over 36,000 feet (11,000 meters) in locations such as the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. On the other hand, it also includes shallow coastal areas and continental shelves.
-
Biodiversity: The ocean is teeming with diverse forms of life, ranging from microscopic phytoplankton to massive whales. It is home to countless marine species, many of which are yet to be fully explored and understood.
-
Economic Importance: The ocean is a valuable resource for human societies, providing food through fishing, supporting maritime transportation and trade, and offering opportunities for tourism and recreation.
-
Climate Regulation: The ocean plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing heat from the sun. It also absorbs a significant portion of the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the impact of greenhouse gases.
-
Oxygen Production: Marine plants, particularly phytoplankton, are responsible for a significant portion of the Earth's oxygen production through photosynthesis.
The ocean is divided into five major geographic regions, known as the "Five Oceans": the Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Each of these oceans has its own unique characteristics, currents, and marine life.
Due to its vastness and remote nature, the ocean remains largely unexplored, and scientists continue to study its depths to understand its impact on the Earth's ecosystems, climate, and overall health.
The ocean is a vast body of saltwater that covers about 71% of the Earth's surface. It plays a crucial role in supporting life on our planet and is an integral part of the Earth's hydrosphere, which includes all water found on or under the surface.
Key characteristics of the ocean include:
-
Saltwater Composition: The water in the ocean contains various dissolved salts, primarily sodium chloride (common table salt). This saltiness is the reason why the ocean is called "saltwater."
-
Global Connectivity: The ocean is not confined to specific regions; it connects all continents and is interconnected through various currents and water movements. This global interconnectivity influences weather patterns and climate across the Earth.
-
Depth Variability: The ocean is incredibly deep, with some areas reaching depths of over 36,000 feet (11,000 meters) in locations such as the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. On the other hand, it also includes shallow coastal areas and continental shelves.
-
Biodiversity: The ocean is teeming with diverse forms of life, ranging from microscopic phytoplankton to massive whales. It is home to countless marine species, many of which are yet to be fully explored and understood.
-
Economic Importance: The ocean is a valuable resource for human societies, providing food through fishing, supporting maritime transportation and trade, and offering opportunities for tourism and recreation.
-
Climate Regulation: The ocean plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing heat from the sun. It also absorbs a significant portion of the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the impact of greenhouse gases.
-
Oxygen Production: Marine plants, particularly phytoplankton, are responsible for a significant portion of the Earth's oxygen production through photosynthesis.
The ocean is divided into five major geographic regions, known as the "Five Oceans": the Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Each of these oceans has its own unique characteristics, currents, and marine life.
Due to its vastness and remote nature, the ocean remains largely unexplored, and scientists continue to study its depths to understand its impact on the Earth's ecosystems, climate, and overall health.
Working